Fertility Financing Options: Real Solutions for Real Families
Fertility Financing Options: Affording the Path to Parenthood
Navigating the emotional and physical journey of fertility treatment is already overwhelming, but adding financial stress can make it even harder. For many individuals and couples, the high cost of treatments like IVF, egg freezing, and fertility medications puts their dreams of parenthood just out of reach. The good news? There are a growing number of fertility financing options designed to help make treatment more affordable, accessible, and less stressful. And we’re here to help you navigate these options and find the best solution for your specific situation.
Top Fertility Financing Options Available Today
Personal Fertility Loans
Many lenders offer personal loans specifically designed for medical or fertility treatments. These loans can cover everything from diagnostic testing to IVF cycles and fertility preservation.
Personal fertility loans offer many benefits:
- Fixed interest rates and monthly payments.
- Quick pre-qualification without affecting your credit score.
- Funds are secured prior to treatment.
Be sure to review the loan’s terms, minimum credit score, interest rates, and any prepayment penalties before committing.
Fertility Clinic Financing Programs
Many fertility clinics partner with financial service providers or offer their own in-house financing. These programs often come with low-interest or interest-free promotional periods, and some even bundle multiple cycles together at a discounted rate.
At the California Center for Reproductive Health, we’ve teamed up with trusted partners like Sunfish, Kindbody, and Carrot to bring you flexible, stress-free financing tailored to your fertility journey.
Health Insurance & Self-Pay Discounts
Insurance coverage for fertility treatments varies dramatically depending on your location and provider. Some plans may cover diagnostic testing or specific procedures, while others exclude fertility entirely.
If you’re paying out of pocket:
- Ask about discounted IVF treatment packages.
- Look for bundled services that include embryo transfers, medications, and lab fees.
- Clarify what’s included to avoid hidden costs.
Don’t forget to inquire about your employer’s fertility benefits: some companies offer assistance through programs like Carrot or Kindbody.
Grants and Financial Assistance Programs
For those who meet income and eligibility criteria, fertility grants can provide significant relief. Organizations such as Baby Quest Foundation, The Cade Foundation, and The Hope for Fertility Foundation offer grants to offset the costs of treatment.
These programs usually require:
- Proof of infertility diagnosis.
- Application essays or medical documentation.
- Demonstrated financial need.
Application windows can be competitive, so start early and follow instructions closely.
Compassionate Care Programs & Nonprofit Assistance
Pharmaceutical companies and nonprofits also offer fertility medication discounts through Compassionate Care programs. These programs help reduce out-of-pocket costs for prescriptions, which can otherwise range from $3,000 to $5,000 per cycle.
These services often provide emotional support alongside financial aid.
Our Trusted Partners: A Closer Look
Sunfish: Personalized Fertility Financing Solutions
Sunfish specializes in providing tailored financial solutions for various fertility treatments, including IVF, egg freezing, surrogacy, and embryo preservation. They offer low-interest loans up to $100,000, with monthly payments starting at $200, depending on the loan amount and terms. Their loan terms range from 2 to 7 years, featuring competitive interest rates, no prepayment penalties, and no origination fees.
Key Features
- IVF Success Program: This program offers a fixed-price IVF cycle with unlimited embryo transfers and a customized refund option for qualified patients, providing financial predictability and peace of mind.
- Comprehensive Support: Sunfish provides assistance and guidance throughout your fertility journey, including access to financial planning tools and discounts on medications.
- Flexible Financing: With a range of loan options, Sunfish caters to diverse financial situations, ensuring that more individuals and couples can access the fertility treatments they need.
Kindbody: Integrated Fertility Care with Flexible Financing
Kindbody offers a comprehensive approach to fertility care, combining medical services with financing options to make treatments more accessible. They provide a range of services, including IVF, egg freezing, embryo banking, and donor services.
Key Features
- Transparent Pricing: Kindbody offers clear pricing for various treatments, with IVF packages ranging from $13,800 to $16,200, depending on the location. These packages include services like ovarian stimulation visits, egg retrieval procedures, fertilization, and embryo storage.
- Financing Through PatientFi: In partnership with PatientFi, Kindbody provides monthly payment plans, allowing patients to start their fertility journey without the burden of upfront costs.
- Insurance and Employer Benefits: Kindbody accepts various insurance plans and collaborates with employers to offer fertility benefits, further reducing out-of-pocket expenses for patients.

Carrot: Employer-Sponsored Fertility Benefits
Carrot partners with employers to provide comprehensive fertility benefits, supporting a wide range of family-building options, including IVF, IUI, egg and sperm freezing, adoption, and surrogacy.
Key Features
- Global Access: Carrot offers services to members worldwide, ensuring access to quality fertility care regardless of location.
- Personalized Support: Members receive tailored guidance throughout their fertility journey, including assistance with treatment planning and access to a network of vetted providers.
- Carrot Card: This benefit allows employees to easily access funds and pay for fertility treatments and services, simplifying the financial aspect of care.
- Data-Driven Outcomes: Carrot’s approach emphasizes better health outcomes, with a focus on single embryo transfers and reduced risks associated with multiple births.
Comparing Financing Plans: What to Look For
Terms & Conditions
Not all financing options are created equal. Look for:
- Low interest rates.
- Minimal or no annual fees.
- No prepayment penalties.
- Clear breakdown of what’s covered.
Make sure you understand whether the funds are disbursed to you or directly to the clinic.
Personalization and Flexibility
Look for plans that offer:
- Budget-friendly monthly payments.
- Tailored repayment lengths.
- Deferred payments or grace periods.
A good program will adjust to your financial situation and allow you to choose your repayment terms.
Hidden Costs and Red Flags
Always request a full cost breakdown from your lender. Ask:
- Are all medications included?
- Will additional embryo transfers cost extra?
- Are there lab or storage fees?
Avoid lenders that charge application fees or require high upfront payments.

Preparing for Your Fertility Journey Financially
How to Estimate Your Costs
The average cost of fertility treatments varies widely. You should estimate:
- IVF cycle (or other fertility treatment) costs.
- Medication expenses.
- Optional services like genetic testing or embryo freezing.
Questions to Ask Your Fertility Clinic
When discussing financing with your fertility clinic, consider asking:
- What are the total estimated costs of the recommended treatments?
- Do you offer in-house financing or partner with third-party lenders?
- Are there any discounts for multiple cycles or bundled services?
- What is included in the quoted price, and are there potential additional costs?
Being informed allows you to plan without surprises.
Creating a Financial Plan
Set a realistic fertility budget that considers:
- Savings contributions
- Insurance coverage or reimbursements
- Monthly loan repayments
Talk to a financial advisor or our fertility specialists to tailor your plan to your goals.

Making Fertility Affordable with the Right Financing Plan
Affording fertility treatment is possible with the right tools and support. From specialized lenders to in-house financing and nonprofit grants, there are options for almost every budget. The key is to plan early, ask the right questions, and explore all available resources.
If you’re unsure where to start, schedule a consultation with our fertility specialists. Our team will review your specific situation, guide you through your choices and help you select a plan that aligns with your medical and financial needs.
Fertility Financing Options FAQ
What is the average cost of fertility treatments?
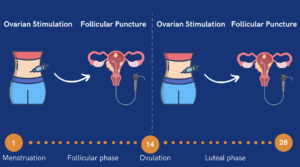
The average cost of fertility treatments varies widely. Fertility medications can cost $1,000 to $5,000 per cycle, while intrauterine insemination (IUI) typically ranges from $300 to $1,000 per cycle. IVF, one of the most common advanced treatments, costs $12,000 to $17,000 per cycle, usually excluding medications, lab work, genetic testing, and embryo storage, which can add $5,000–$10,000 more. Costs increase further if multiple cycles or donor services are needed.
What is the best way to finance fertility treatments?
The best option depends on your financial situation, treatment plan, and timeline. Many patients use a combination of personal loans, clinic payment plans, and employer-sponsored benefits. Fertility-focused lenders often provide low-interest loans tailored to treatments like IVF and egg freezing. Bundled packages from clinics can also reduce overall costs. The key is to evaluate all your options and choose a plan that balances affordability with flexibility. Consulting a fertility financing specialist can help guide your decision.
What factors affect my eligibility for fertility financing?
Your credit score, income level, and debt-to-income ratio are key factors lenders consider. Some financing programs also require a co-signer or a minimum credit score. Grant programs often assess financial need, fertility diagnosis, and treatment urgency. Each lender or assistance program has unique eligibility criteria. Review these carefully before applying to improve your chances of approval.