What Is IVF Fertility Treatment?
When you start to research your options in fertility treatment, one of the first questions you’re likely to ask is “What is IVF fertility treatment?” IVF or in vitro fertilization is a form of assisted reproductive technology that involves combining eggs with sperm outside the body in a lab and returning the fertilized egg to the uterus. There are several steps involved in this form of treatment, and these steps work together to give you a better chance to have a healthy and successful pregnancy.
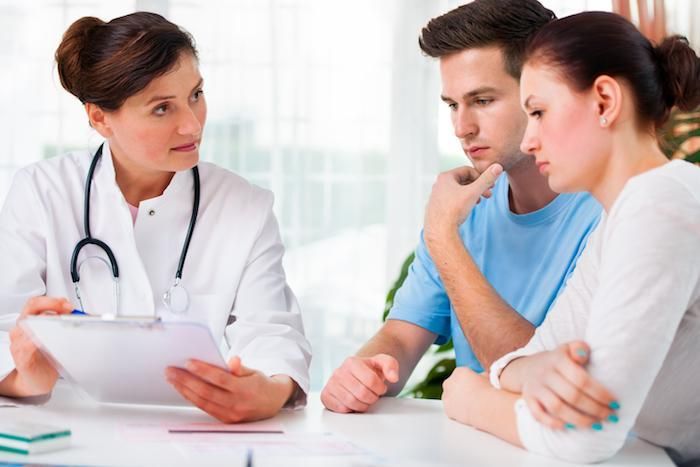
The experienced staff at the Center for Reproductive Health understand how overwhelming it can be to have difficulty conceiving. They provide expert guidance on fertility treatment options and can answer any questions you may have.
Who May Benefit from IVF Fertility Treatment?
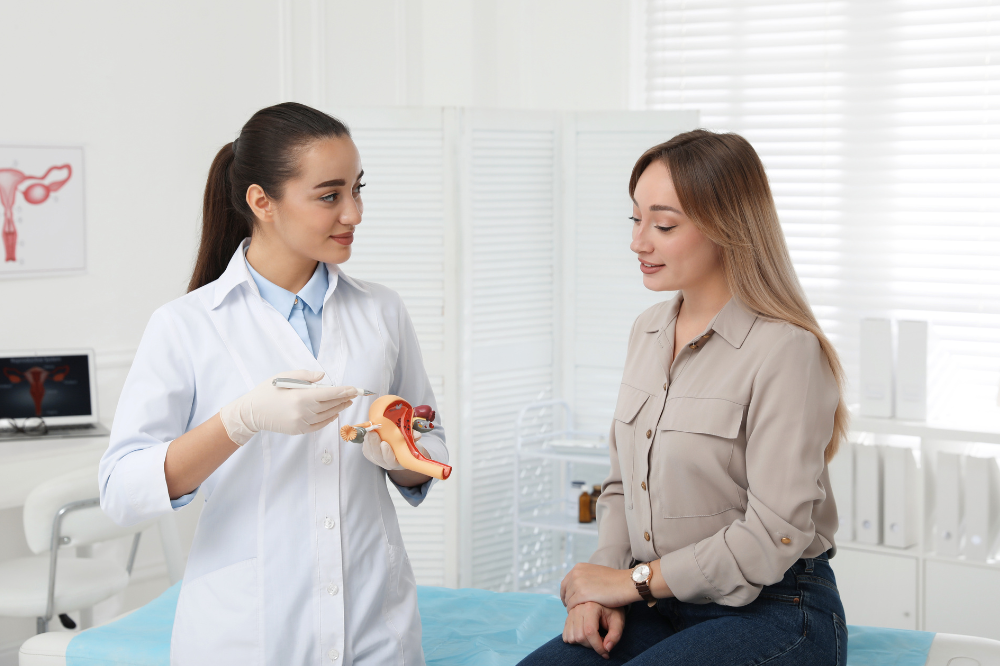
Before undergoing IVF, you and your partner are both evaluated to determine the cause of infertility. Difficulty getting pregnant may happen because of issues with either partner or both together. IVF may benefit people with many different challenges such as:
- Uterine fibroids
- Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes
- Ovulation disorders
- Endometriosis
- Decreased sperm count or poor sperm mobility
Women over the age of 40 who have had difficulty conceiving may benefit from IVF. It’s not always easy to pinpoint the reason for being unable to conceive, and IVF may benefit those who have unexplained infertility.
The Steps of IVF Fertility Treatment
The process involved in IVF takes several weeks and the total amount of time needed can vary from one patient to the next. Injectable hormones are used to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. This is done over the course of several days. Eggs that are produced are triggered to mature so that they can be harvested during a minor surgical procedure.
After eggs have been harvested, they are mixed with sperm from the patient’s partner or from a sperm donor. Fertilized eggs are cultured in the lab for a few days so they can develop into embryos. One or more embryos are then implanted into the uterus by your doctor.
After approximately ten to twelve days, a pregnancy test is done. If the test is negative, you’ll probably get your period within a week, and you’ll discuss the next steps with your doctor or fertility counselor.
Other Considerations
Before treatment with IVF, you’ll need to consider how many embryos will be transferred since there’s a risk of multiple births if more than one embryo is transferred. You’ll also need to decide what to do with extra embryos. Some may be frozen for future use, although they may not all survive this process.
A full cycle of IVF takes several weeks and more than one cycle may be needed for a successful pregnancy. You have a better chance of good results if you’re under the age of 35. Fertility specialists work with you to discuss how you can improve your chances of getting pregnant using IVF fertility treatment.
To learn more about IVF, contact the team at the Center for Reproductive Health. We provide the most advanced fertility treatment options available and are committed to improving your chances of having a baby.